What are Marketing Intermediaries? Definition and examples

Producing a good product is a top concern for business people, but mastering the distribution channel that gets the product to the final buyer is just as important. In particular, Marketing Intermediaries connect producers and consumers, which is applied and successful by many businesses.
In today’s article, CleverAds will introduce and analyze to help you better understand the term Marketing Intermediaries.
1. What are Marketing Intermediaries?
A marketing or distribution channel is a group of interdependent organizations and individuals bringing a product to the consumer.
In this process, the appearance of a third party to assist in the distribution of products to customers is called Marketing Intermediaries.
Marketing Intermediaries (also known as Distribution Intermediaries) are one or more organizations and individuals that act as a bridge between manufacturers and consumers in the distribution of products.
Marketing intermediaries assist manufacturing businesses in marketing, selling, and shipping products to customers.
There are many reasons manufacturers choose Marketing Intermediaries over direct distribution. This means giving up control of some of the work in selling the product. However, thanks to their extensive industry relationships, in-depth experience, and various support tools, Marketing intermediaries bring more benefits to manufacturers than if they dealt with themselves directly.
Enterprises need to analyze the characteristics and activities of marketing intermediaries to establish appropriate cooperation terms and maintain a positive relationship between the two parties. At the same time, businesses sometimes need to adjust and change the terms of product distribution to suit the activities of marketing intermediaries.

2. Examples of Marketing Intermediaries
2.1. Marketing Agents
Marketing agents (Marketing Units) are responsible for finding and attracting units in the distribution chain together. They act as marketers or manufacturer representatives and do not own the product being sold. Examples are marketing research agencies, advertising agencies, media agencies, newspapers, consulting marketing solutions to support businesses, etc.
The field of activity of Marketing agents is extensive throughout the international trade industry. When companies can’t reach their target customers directly, they hire marketing agents to help them sell. The intermediary will be paid a commission from the transaction and will only connect the buyer with the seller.
An example of a Marketing agent is a Travel agent. They advise you on the best places to visit during your travels and provide visa application processing and flight booking services. In the process, they also act as marketing intermediaries for hotels and airlines.
They sell on behalf of hotels and airlines to customers that these companies cannot reach directly. Travel agents earn a fixed percentage of commission for each successful transaction.
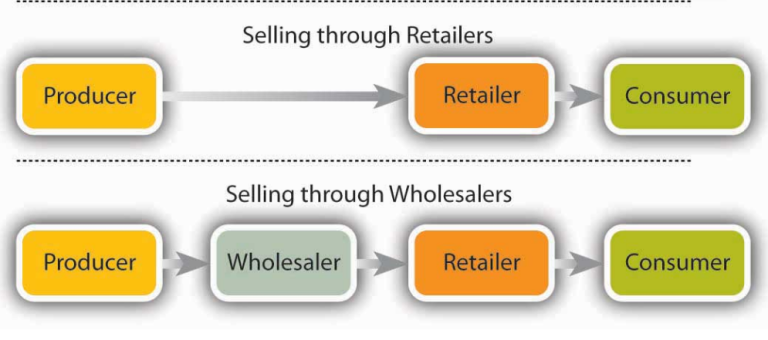
2.2. Wholesaler
A wholesaler is an intermediary that buys goods in bulk from a producer and then sells them to a retailer in smaller quantities.
Large-scale manufacturing companies cannot sell directly to consumers. This is because they need the infrastructure and scale of logistics to reach and deliver their products to thousands, sometimes millions of customers.
Example in the pharmaceutical industry: A drug manufacturer supplies products in the bulk of 1000 boxes of a single sale. But a typical pharmacy or hospital only requires a small quantity for a particular drug, only a tiny amount, like 10-20 boxes of medicine a month. So a wholesaler buys 1000 units of the product from the manufacturer for $1/unit and then sells it to multiple retailers for $1.25/unit.
In this way, a wholesaler sells goods to different retailers at a higher price and profits from the difference. In contrast, a retail medical store can quickly find a particular drug from a wholesaler in the required quantities. It is also more accessible for the manufacturer to distribute and sell.
2.3. Distributor
The Distributor (Distributor) acts as an intermediary between the manufacturer and the retailer, promoting the manufacturer’s products and selling the products to retailers and wholesalers. Their job is to get products from the manufacturer to the retailer and find new market opportunities and ways to expand their brand.
A distributor is a combination of wholesalers and marketing agents.
They are hired to market the manufacturer’s products and are paid a commission for their sales. However their mode of operation is mass, and their target audience is retailers.
The manufacturer can formally agree with the distributor that party B will only promote and sell goods that the company manufactures or endorses. The manufacturing company should hire a distributor.
Take Gillette as an example. A distributor will only work with Gillette products, stores, and resell in the future, earning a commission or transaction fee from each sale they make.
2.4. Retailer
A Retailer is the final intermediary link in the supply chain that buys products from a manufacturer or wholesaler and then sells them to the last buyer. These are the people who best understand the needs and wants of their customers. As a result, they have a rich and diverse store system, ensuring the availability of goods and creating the best conditions for buyers.
However, the increasing cost per unit product continues as the retailer sells each unit at a higher price to the customer. Therefore, the retail business promotes products to many people and conveniently helps them make purchases.
Supermarkets, bookstores, pharmacies, and online shopping sites are all examples of retailers.
Take Walmart as an example; there are many products in one place for you to choose and buy quickly. However, Walmart imports goods from wholesalers in bulk and resells them to consumers at a higher price.
Another example of a retail intermediary is an online shopping store like Amazon, Alibaba, or Shopee. Any shopping site that ships directly to the customer is an e-commerce retailer. They source their products in bulk from wholesalers and sell them to the end consumer at retail prices.
3. Conclusion
Marketing Intermediaries are a vital link for products to reach consumers and provide more support to manufacturers to reduce costs and risks.


